A radiology technician plays an essential role in modern healthcare by helping physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. Their work involves operating imaging equipment such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and mammograms to capture detailed images of patients’ internal structures.
Radiology technicians work closely with radiologists, healthcare teams, and patients to ensure accurate images are obtained for diagnostic purposes. As this profession continues to evolve with advancements in medical technology, the demand for trained radiology technicians is on the rise.
This article will guide you through what it takes to become a radiology technician, the responsibilities of the role, educational requirements, and career prospects. By the end, you’ll have a deep understanding of what this career entails and whether it aligns with your professional goals.
What Does a Radiology Technician Do?
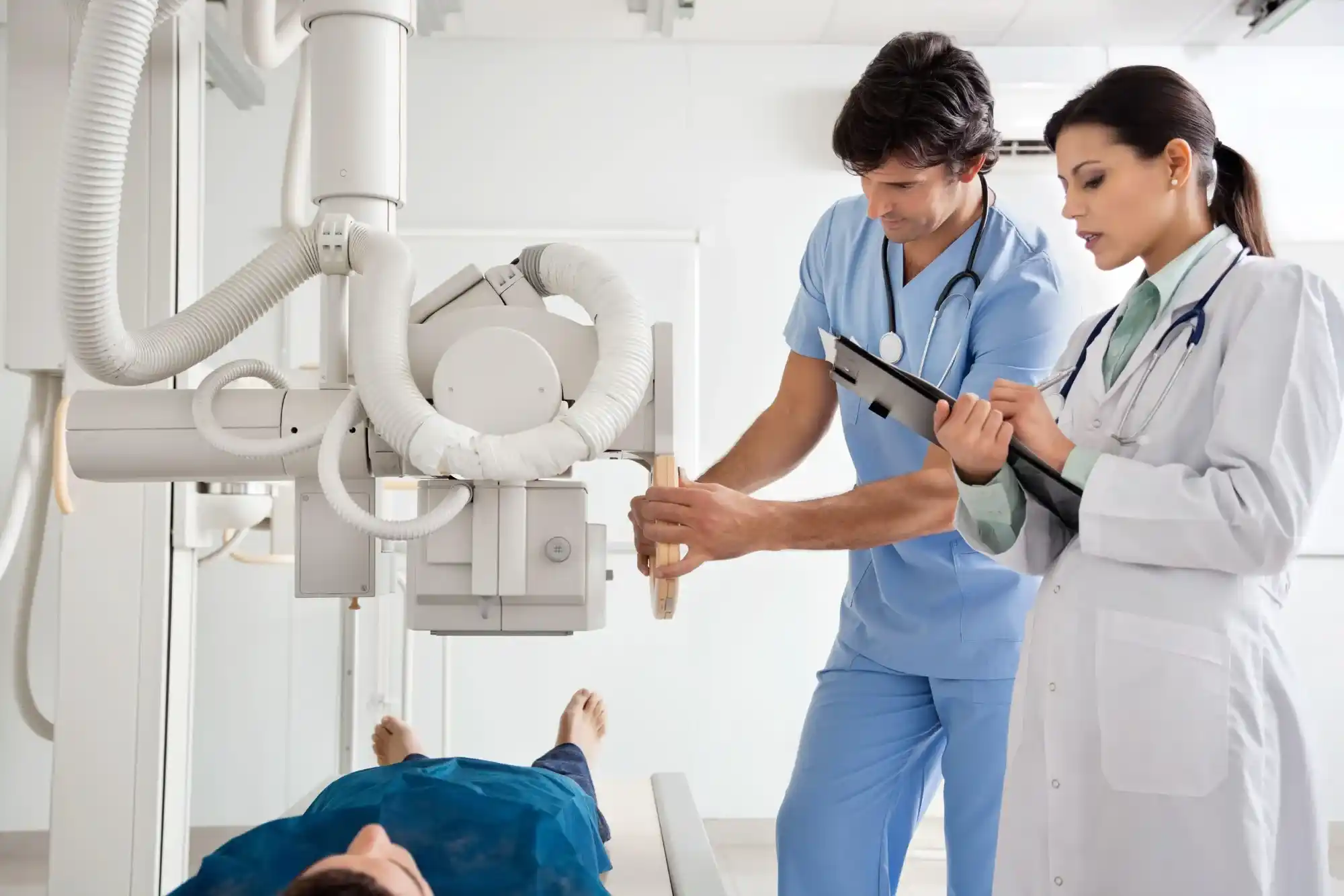
Radiology technicians, also known as radiologic technologists, are skilled professionals trained to operate diagnostic imaging equipment and capture clear images of patients’ internal organs and systems. These images are used by physicians to diagnose and treat various medical conditions. A radiology technician must not only have a deep understanding of how to operate imaging machinery but also ensure patient safety by minimizing exposure to radiation. Here’s a closer look at their duties:
Primary Responsibilities
- Operating Imaging Equipment: A radiology technician is responsible for positioning patients and ensuring the correct part of the body is imaged.
- Patient Preparation: Preparing patients for procedures, explaining the process, and answering any questions they may have.
- Safety Protocols: Ensuring patient safety by adhering to protocols that minimize radiation exposure.
- Maintaining Equipment: Performing routine maintenance on imaging equipment to ensure optimal functionality.
- Collaboration with Healthcare Professionals: Working closely with radiologists and other healthcare providers to produce accurate diagnostic images.
Educational Requirements and Training
High School Diploma or GED
The first step to becoming a radiology technician is obtaining a high school diploma or equivalent. Strong grades in science, math, and health-related courses will provide a solid foundation for further studies in the field.
Enroll in an Accredited Radiologic Technology Program
After completing high school, prospective radiology technicians must enroll in an accredited radiologic technology program. These programs are offered by community colleges, technical schools, and universities and typically take between 18 months to 4 years to complete, depending on the degree pursued.
- Associate Degree: Most radiology technicians earn an Associate of Applied Science (AAS) in Radiologic Technology, which takes around two years to complete.
- Bachelor’s Degree: Some technicians choose to pursue a bachelor’s degree for advanced career opportunities.
Clinical Experience
Clinical experience is a critical component of radiology technician training. It allows students to practice their skills in a real-world setting under the supervision of licensed professionals. During clinical rotations, students work with actual imaging equipment, interact with patients, and observe how experienced technicians operate in healthcare environments.
Obtain Certification and Licensure
After completing a radiologic technology program, aspiring radiology technicians must obtain certification and licensure to practice. Certification is typically obtained through the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT). Most states require radiology technicians to be licensed, and the requirements vary by state.
Continuing Education
Once certified, radiology technicians must participate in continuing education to maintain their certification. This ensures they stay up-to-date with the latest technological advances and medical practices in the field.
Skills Needed to Succeed as a Radiology Technician
To be successful in the field of radiology, technicians must possess a combination of technical skills, interpersonal abilities, and an understanding of safety protocols. Below are some key skills necessary for the job:
Technical Skills
- Operating Imaging Equipment: Mastery of X-ray machines, CT scanners, MRI machines, and other diagnostic equipment.
- Anatomical Knowledge: Understanding of human anatomy to capture accurate images for physicians.
- Radiation Safety: Knowledge of radiation protection to minimize exposure to both the patient and technician.
- Medical Terminology: Familiarity with medical terminology and procedures is crucial when interacting with physicians.
Interpersonal Skills
- Communication: Radiology technicians must effectively communicate with patients and healthcare teams.
- Patient Care: Providing compassionate care and making patients feel comfortable during potentially stressful procedures.
- Attention to Detail: Ensuring that imaging procedures are conducted accurately and efficiently.
Radiology Technician Salary and Job Outlook
The field of radiology offers competitive salaries and promising job prospects, with demand for radiology technicians expected to grow in the coming years.
Salary
The salary of a radiology technician varies depending on factors such as experience, location, and education level. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual salary for radiology technicians in the U.S. is around $63,000. However, those with advanced certifications or specializations may earn significantly more.
Job Outlook
The employment of radiology technicians is projected to grow by 9% from 2022 to 2032, which is faster than the average for all occupations. This growth is largely due to an aging population that requires more medical imaging services.
Job Opportunities
Radiology technicians can find employment in a variety of healthcare settings, including:
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Imaging Centers
- Physician’s Offices
- Outpatient Care Centers
- Research Facilities
Specializations in Radiology Technology
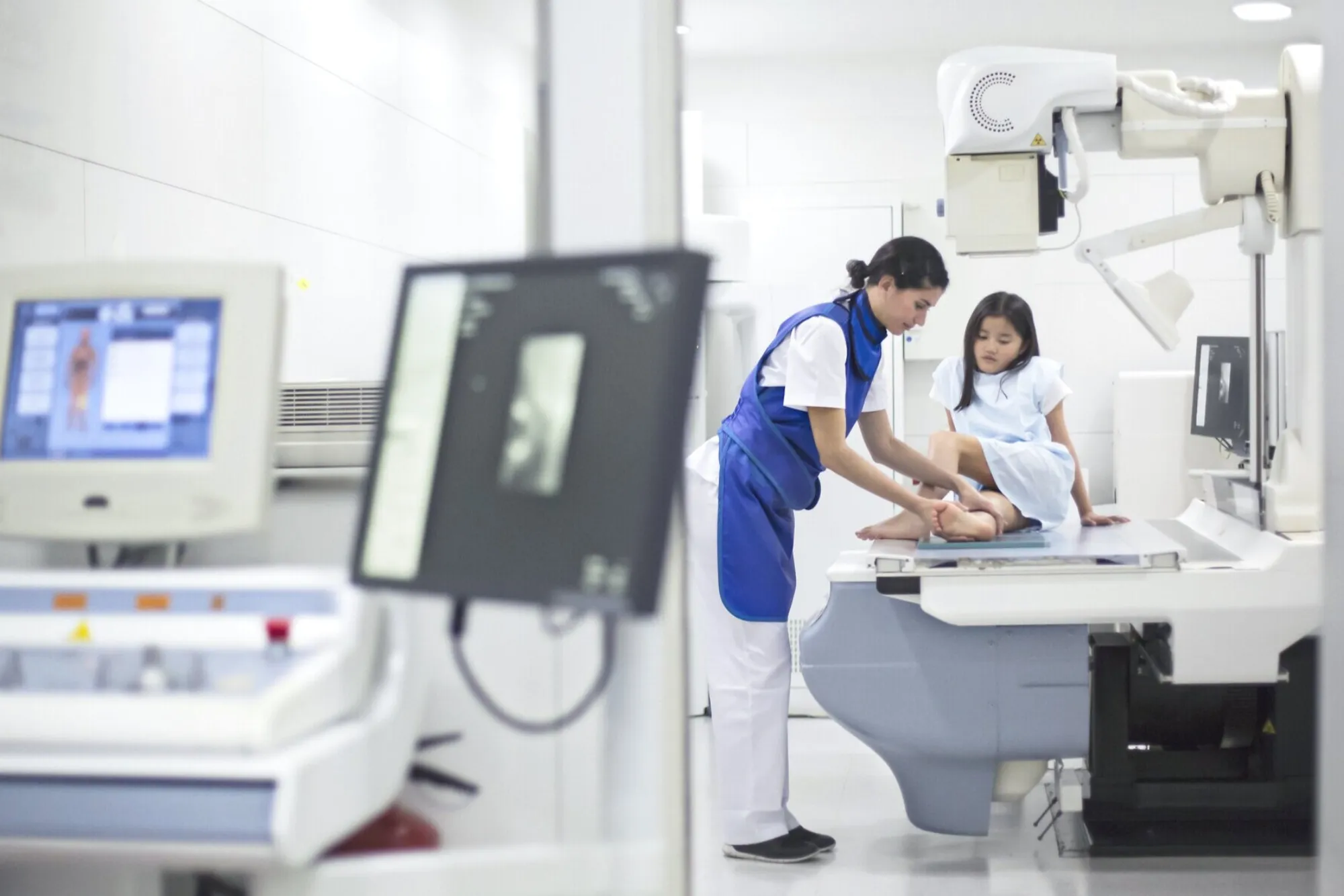

While most radiology technicians begin their careers in general radiologic technology, there are several areas of specialization that can offer additional career opportunities. Some of these include:
- MRI Technologist: Specializes in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body.
- CT Technologist: Operates computed tomography (CT) scanners, which create cross-sectional images of the body.
- Mammography Technologist: Specializes in imaging the breast for early detection of cancer or other abnormalities.
Challenges Faced by Radiology Technicians
While the career of a radiology technician is rewarding, it is not without its challenges. Some common challenges include:
- Physical Demands: Radiology technicians may spend long hours on their feet and may need to assist in moving patients who have limited mobility.
- Emotional Stress: Working with patients who are anxious or in pain can be emotionally taxing.
- Exposure to Radiation: Although safety protocols are in place, radiology technicians are still exposed to low levels of radiation. Proper use of protective equipment is essential to mitigate risk.
Table: Comparison of Radiology Technician Specializations
| Specialization | Primary Duties | Average Salary (Annually) | Required Certification |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRI Technologist | Operates MRI machines, produces detailed images of organs and tissues. | $73,000 | MRI Certification from ARRT |
| CT Technologist | Uses CT scanners to create cross-sectional images of the body. | $67,000 | CT Certification from ARRT |
| Mammography Technologist | Focuses on imaging the breast for cancer screening. | $68,000 | Mammography Certification from ARRT |
| General Radiology | Performs X-rays and basic imaging procedures across different body systems. | $63,000 | Radiography Certification from ARRT |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between a radiology technician and a radiologist?
A radiology technician is responsible for operating imaging equipment and preparing patients for imaging procedures, while a radiologist is a medical doctor who interprets the images to diagnose and treat conditions.
How long does it take to become a radiology technician?
It typically takes around two years to earn an associate degree in radiologic technology, plus additional time for certification and licensure.
Is the radiology technician field growing?
Yes, the demand for radiology technicians is expected to grow by 9% over the next decade due to the increasing need for diagnostic imaging services.
Do radiology technicians need continuing education?
Yes, radiology technicians must participate in continuing education to maintain their certification and stay updated with technological advancements.
What safety measures do radiology technicians take to reduce radiation exposure?
Radiology technicians follow strict safety protocols, such as wearing lead aprons and shields, using protective barriers, and limiting exposure time to minimize the risk of radiation.
Becoming a radiology technician offers a dynamic and rewarding career in healthcare. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can begin your journey toward a fulfilling profession that combines cutting-edge technology with patient care. The radiology technician role is crucial in diagnosing and treating medical conditions, making it an invaluable part of the healthcare industry.



